Why is Australia’s rank so low when it comes to innovation?

The ability to innovate is one of the most important factors in economic growth. It increases productivity by making it possible to produce more with the same amount of input or investment as before.
Putting it simply, when productivity increases, more products and services are produced, which results in higher economic growth.
Australia has a long history of innovation and entrepreneurship, but it is ranked below many other countries in terms of innovation performance.
https://www.globalinnovationindex.org/userfiles/file/reportpdf/GII-2021/GII_at_a_glance.pdf
The Global Innovation Index (GII) is a new index that measures the innovation performance of nations in the world. It is published by the United Nations Agency – World Intellectual Property Organisation (WIPO) and is an important tool for understanding how countries are performing when it comes to innovation.

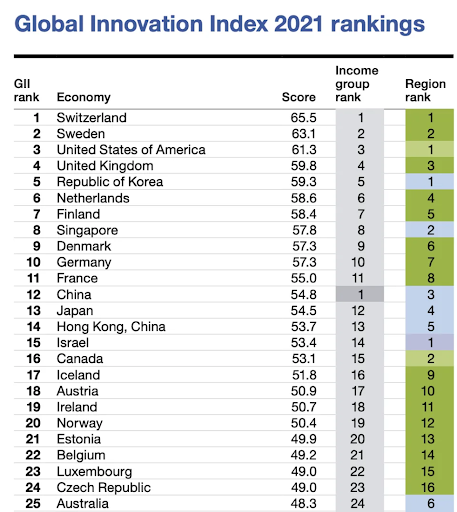
Australia ranks at number 25 in the 2021 edition of GII, below countries like China, Japan, Germany, France, Singapore, United Kingdom, Sweden and South Korea in innovation performance. This is because a number of factors, such as:
- Australia does not have enough funding and support for research and development.
- There is a lack of skilled workers to create innovative ideas
- Fewer top-flight academic institutions compared to its rival countries
- Small population
- Less emphasis on commercialisation and effective monetisation of innovation in all industries
- Having a number of structural and cultural barriers
- Communication gap between the academic, industrial and political sectors
The Australian political system itself stands as the most significant structural barrier to successful innovation, according to a report from the United States Studies Centre at the University of Sydney.
The three-year political cycle in Australia, as well as subsequent administrations, have a tendency to sabotage rules established by prior governments. Every new political party in power has a strong desire to modify policies, initiatives, and budgets, resulting in inconsistency in the area of innovation.
The seven pillars of the Global Innovation Index (GII) and what they represent

How world economies have fared in innovation in 2021
What factors contributed to Switzerland’s high ranking on the list?
Dynamic innovation systems combined with efficiency to turn innovation ‘inputs’ into innovation ‘outputs’ are found in the economies that have consistently moved up the Global Innovation Index (GII) rankings over the past decade. These economies also exhibit balanced and strong performance across all GII pillars.
This year, only 15 economies were included in the ranking, representing only 11 per cent of all economies.
Switzerland, the leading country, not only provides a fertile basis for invention but also serves as an inspiration for many innovative ideas.
Aside from substantial investment in research and development, Switzerland’s strong position is attributable to the high quality of its people resources and the presence of numerous local universities.
Furthermore, it fared exceptionally well as a result of the country’s stable political system, favourable regulatory framework, and well-developed infrastructure.
What steps can Australia take to overcome these obstacles?
The Australian government has put a lot of emphasis on innovation and entrepreneurship in recent years, but they have not been able to produce the desired results. Australia’s innovation performance is an issue that needs to be addressed. It is an issue that will benefit both Australia, as well as other countries around the world.
The Australian government needs to invest more in innovation and education to make sure Australia can be a country that leads the world in innovation performance.
The establishment of an independent and permanent institution to oversee the formulation and implementation of a national plan for science and innovation in Australia is one possible solution to the problem.
This would not only increase communication between sectors, but it would also serve as a point of continuity for long-term planning and funding efforts as well.
The Chinese mainland, on the other hand, is home to 17 of the world’s most important research and technology clusters.
What is the purpose of this evaluation?
The Global Innovation Index’s overall formula for measuring an economy’s innovative capacity and output provides clarity for decision-makers in government, business, and other organisations as they look forwards to developing policies that will enable their people to invent and create more efficiency in the future.